Without them, Earth's surface would average about 33 °C colder, which is about 59 °F below the present average of 14 °C (57 °F)"The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone Greenhouse gases greatly affect the temperature of the Earth;Greenhouse Effect Shown above is an Infrared Map of the Earth Red areas represent regions of high heat retention in the atmosphere This is an equatorial band because that is where the atmosphere has the most water vapor The earth has a natural greenhouse effect due to trace amounts of H 2 0 and CO 2 that naturally occur
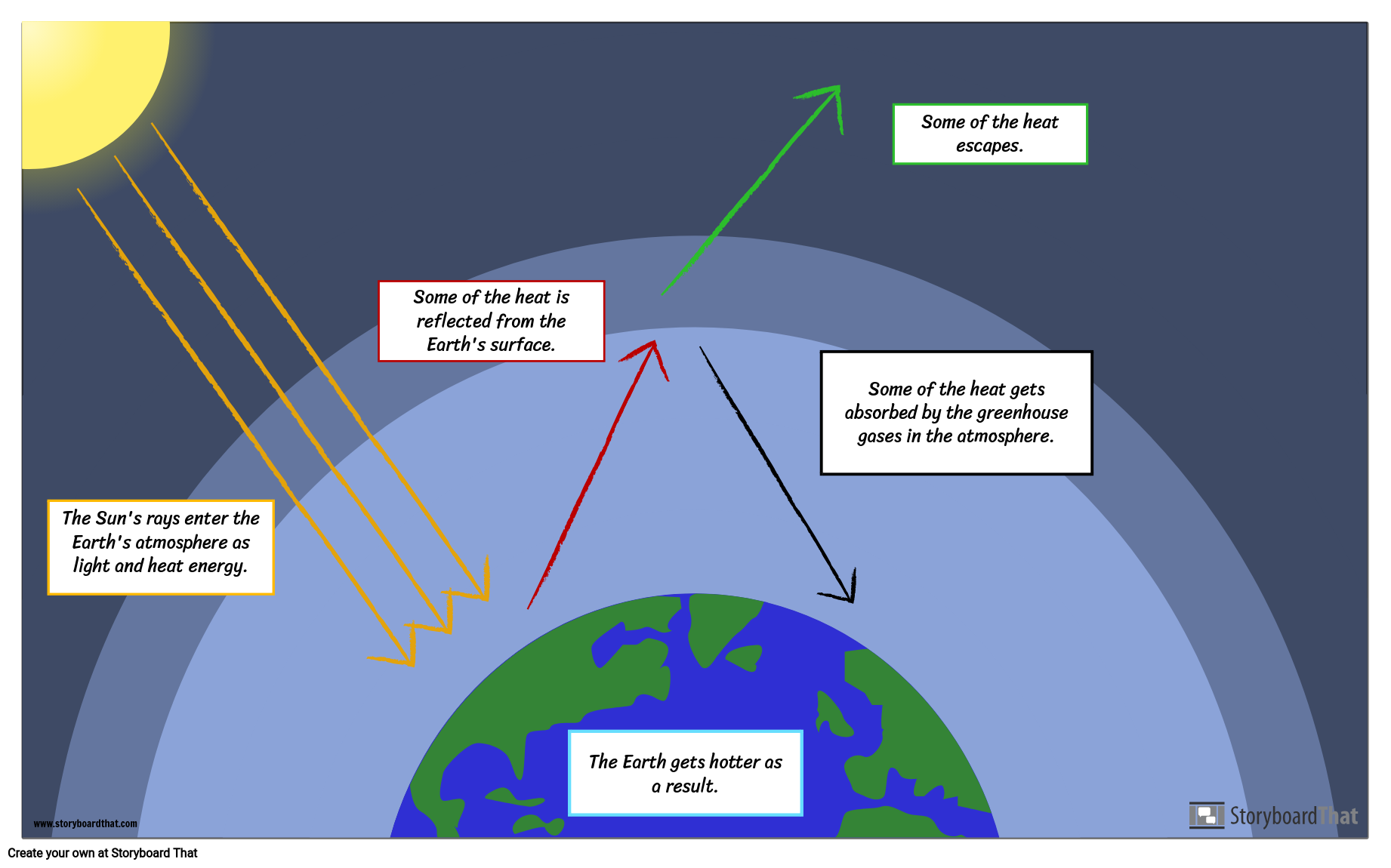
Creating A Greenhouse Effect Diagram
Atmosphere diagram greenhouse gases
Atmosphere diagram greenhouse gases-The list includes H2O, CO2, CH4, N2O, O3, and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)Main Greenhouse Gases Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs lived



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja
Some of these gases (like methane) are considerably more shortlived in the atmosphere than CO 2, persisting for decades rather than centuries Such complications are often dealt with through the concept of global warming potential (GWP), which takes into account both the radiative properties of a particular greenhouse gas molecule and theGreenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclearGreenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases (To a lesser extent, surfacelevel ozone, nitrous oxides, and fluorinated gases
The 'greenhouse effect' is the warming of climate that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere resemble glass in a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass into the 'greenhouse,' but blocking Earth's heat from escaping into space The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effectGreenhouse gases are gases—like carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane, and nitrous oxide—that keep the Earth warmer than it would be without them The reason they warm the Earth has to do with the way energy enters and leaves our atmosphere When energy from the sun first reaches us, it does so mainly as lightData Trends in CO 2, CH 4, N 2 O, SF 6 Obs ervation Pack age Marine Boundary Layer Reference Data Archive Products CarbonTracker CO 2 CarbonTracker CH 4 CarbonTracker Lagrange Power of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Index Information Figures Education How CO 2 is Measured Isotope Measurements WMO Standard Gas Comparisons
Greenhouse gas concentrations Total Time Two 45minute class periods Prior Knowledge It is helpful for students to have covered the different types of energy, and energy transformation, particularly from light to heat, as this transformation is an important process in understanding how greenhouse gases retain heat in the atmosphere Materials The natural greenhouse effect is a phenomenon caused by gases naturally present in the atmosphere that affect the behaviour of the heat energy radiated by the sun In simple terms, sunlight (shortwave radiation) passes through the atmosphere, and is absorbed by Earth's surface This warms Earth's surface, and then Earth radiates some ofThe diagram gives more details about this process, called the greenhouse effect How the greenhouse effect works electromagnetic radiation at most wavelengths passes through the Earth's atmosphere




How Exactly Does Carbon Dioxide Cause Global Warming You Asked




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts
Carbon dioxide Methane Ozone Nitrous oxide Chlorofluorocarbons Greenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat They get their name from greenhouses A greenhouse is full of windows that let in sunlight That sunlight creates warmthThe graph to the right shows which activities produce the most greenhouse gases in the United States These greenhouse gases don't just stay in one place after they're added to the atmosphere As air moves around the world, greenhouse gases become globally mixed, which means the concentration of a greenhouse gas like carbon dioxide is roughly the same no matterCarbon dioxide (CO 2) is the primary greenhouse gas emitted through human activities In 19, CO 2 accounted for about 80 percent of all US greenhouse gas emissions from human activities Carbon dioxide is naturally present in the atmosphere as part of the Earth's carbon cycle (the natural circulation of carbon among the atmosphere, oceans, soil, plants, and animals)




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




How To Explain The Greenhouse Effect To Kids With Printables Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Effect Greenhouse Gases
Here is why If the atmosphere contains too much of these gases, the whole Earth becomes a hotter and hotter greenhouse The atmosphere holds onto too much of the heat at night instead of letting it escape into space Then, the next day, the Sun heats Earth's surface even more If the atmosphere works too well as a greenhouse, each day gets a Greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth's surface Water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone are greenhouse gases The main gases responsible for the greenhouse effect include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and water vapor (which all occur naturally), and fluorinated gases




The Greenhouse Effect World101



Greenhouse Gas Vector Art Icons And Graphics For Free Download
Let's consider the principal GHGs one at a time, starting with water vapor, the most abundant greenhouse gas in the atmosphere according to NOAA's National Climatic Data Center (NCDC) Water Vapor Carbon Dioxide (CO 2) Methane (CH 4) Nitrous oxide (N 2 O) Fluorinated Gases (HFCs, PFCs, SF 6) References and Resources The greenhouse effect arises from Earth's atmosphere Visible light from the sun, as well as invisible ultraviolet and infrared wavelengths, can penetrate the gaseous layer that blankets our worldThe atmosphere today contains more greenhouse gas molecules, so more of the infrared energy emitted by the surface ends up being absorbed by the atmosphere Since some of the extra energy from a warmer atmosphere radiates back down to the surface, Earth's surface temperature rises By increasing the concentration of greenhouse gases, we are
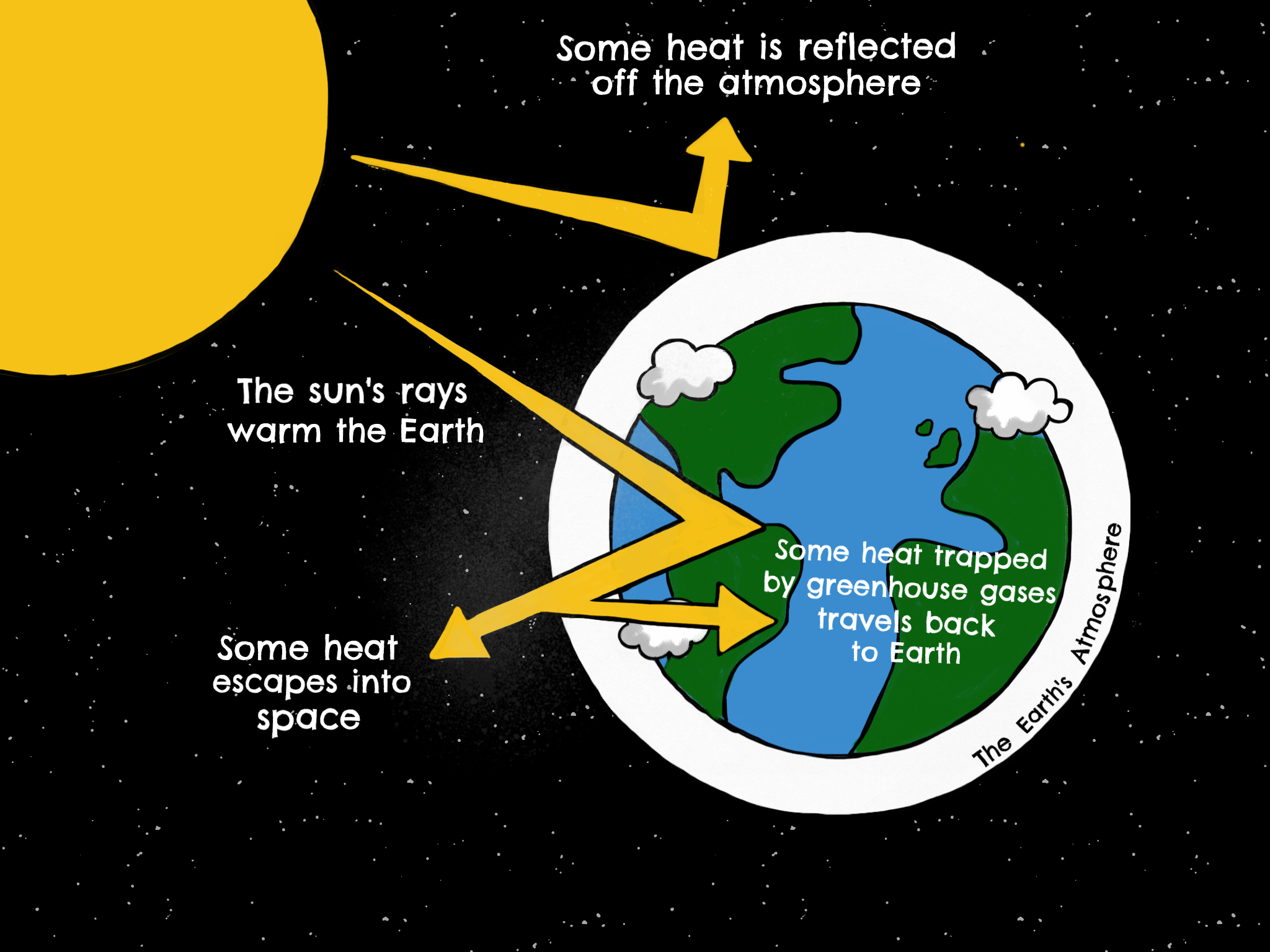



Introduction To Greenhouse Gases Industry And Climate Change



The Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect works much the same way on Earth Gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, trap heat similar to the glass roof of a greenhouse These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases During the day, the Sun shines through the atmosphere Earth's surface warms up in the sunlight At night, Earth's surface cools, releasing heat back into the air But some of the heat is trapped by the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere The basic explanation for why CO2 and other greenhouse gases warm the planet is so simple and has been known science for more than a century Our atmosphere is transparent to visible light — the rainbow of colors from red to violet that make up natural sunlight Graphic A simplified animation of the greenhouse effect En la gráfica se comparan los cambios en la temperatura de la superficie global (línea roja) y la energía del Sol que recibe la Tierra (línea amarilla) en vatios (unidades de energía) por metro cuadrado desde 10




The Greenhouse Effect Draw And Label A Diagram Of The Carbon Cycle Do It Now Ppt Download
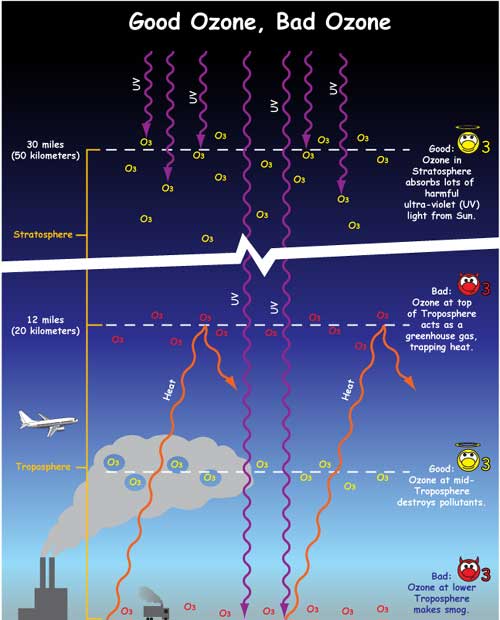



The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids
While the Earth's (dry) atmosphere is predominantly composed of nonIR absorbers, N 2 (78%), O 2 (21%), and Ar (~09%), the 01% of remaining trace gases contains many species that absorb IR The absorptions by CO 2 , CH 4 , N 2 O, and O 3 are shown in the schematic diagramThere are many greenhouse gases but these are some of the most important water vapour, H2O carbon dioxide, CO2 methane, CH4 nitrous oxide, N2O CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons)Human Activity and the Greenhouse Effect What greenhouse gases do humans generate?




File Earth S Greenhouse Effect Us Epa 12 Png Wikimedia Commons




Greenhouse Gases Effect On Climate U S Energy Information Administration Eia
In the troposphere—the layer of the atmosphere near ground level—ozone is an air pollutant that is harmful to breathe, a main ingredient of urban smog, and an important greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change (see the Climate Forcing indicator) Unlike the other major greenhouse gases, tropospheric ozone only lasts for days to weeks, so levels often vary by The process of gases in the Earth's atmosphere trapping the Sun's heat is known as the greenhouse effect Due to this process, the Earth is much warmer than it would be without an atmosphere The greenhouse effect is one of the411 Sources of Greenhouse Gases 243 412 Atmospheric Chemistry and Feedbacks 245 413 Trace Gas Budgets and Trends 246 414 Atmospheric Lifetimes and TimeScales 247 42 Trace Gases Current Observations, Trends and Budgets 248 421 NonCO 2 Kyoto Gases 248 4211 Methane (CH 4) 248 4212 Nitrous oxide (N 2O) 251 4213
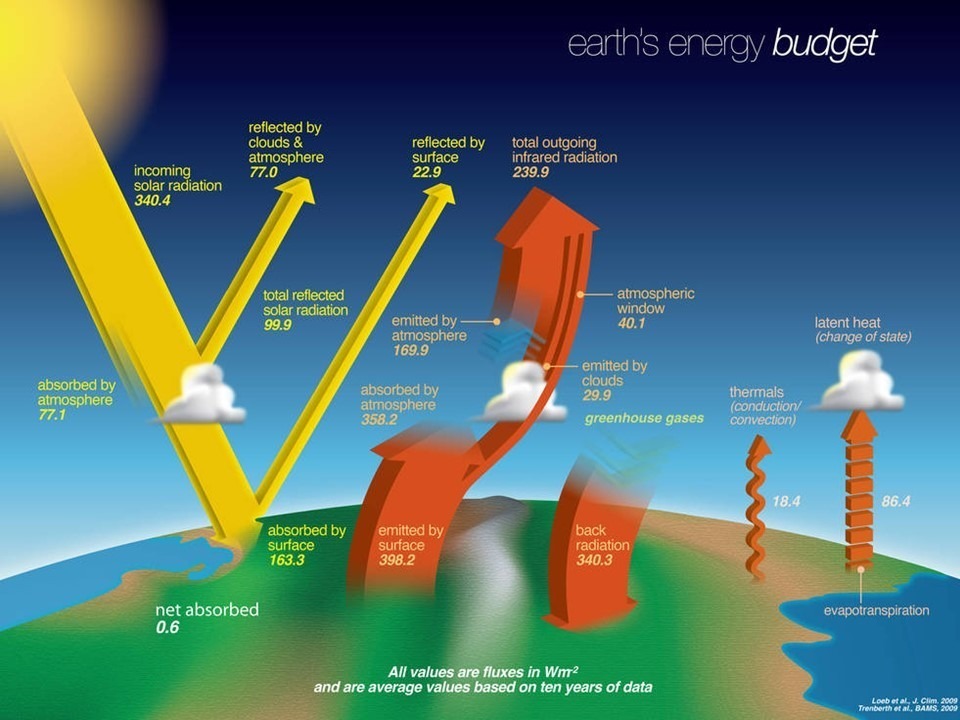



Comments On Dr Ollila S Claims That Greenhouse Effect Calculations Violate Energy Conservation Roy Spencer Phd




Greenhouse Effect High Res Stock Images Shutterstock
Atmospheric methane is the methane present in Earth's atmosphere Atmospheric methane concentrations are of interest because it is one of the most potent greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere Atmospheric methane is rising The year global warming potential of methane is 84 That is, over a year period, it traps 84 times more heat per mass unit than carbon dioxideMost other constituents, found in trace quantities in the atmosphere, are greenhouse gases The important greenhouse gases are those present at concentrations sufficiently high to absorb a significant fraction of the radiation emitted by the Earth; Students build and examine a diagram of Earth's energy balance, discussing the inputs, transfers, and outputs of the system They complete lab activities to demonstrate the natural greenhouse effect and the enhanced greenhouse effect due to the addition of greenhouse gases




Greenhouse Effect Accessscience From Mcgraw Hill Education




Climate Change Basics Ag Matters
Energy absorption by the atmosphere stores more energy near its surface than it would if there was no atmosphere The average surface temperature of the moon, which has no atmosphere, is 0°F (18°C) By contrast, the average surface temperature of the Earth is 59°F (15°C) This heating effect is called the greenhouse effect Simplified diagram showing how Earth transforms sunlight into infrared energy Greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane absorb the infrared energy, reemitting some of it back toward Earth and some of it out into space Greenhouse Gases Methane, Carbon Dioxide Share of Global GHG Emissions 3% A man scavenges for waste to recycle at a garbage dump in Linfen, China Landfill sites like this produce greenhouse gases because rotting organic waste like food waste emits methane which warms the atmosphere unless it is captured



Untitled Document




The Greenhouse Effect World101
The answer lies in the greenhouse effect — gases in our atmosphere (including CO 2, CH 4 (methane) and H 2 O water vapor) trap much of the emitted heat and then reradiate it back to Earth's surface This means that the energy leaving our planet from the top of the atmosphere is less than one would expect given the known temperature of ourThe greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth's surface When the Sun's energy reaches the Earth's atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and reradiated by greenhouse gases Greenhouse gases include water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and some artificial chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gases—collect in Earth's atmosphere These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide , methane , nitrogen oxide, and fluorinate d gases




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




What Is Climate Change Climate Assembly
A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (H 2 O), carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), and ozone (O 3) The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides Greenhouse gases arise naturally, and are part of the makeup of our atmosphereEvery day we generate greenhouse gases through interaction with factories, agriculture, and cars Our activities produce four major greenhouse gases (Figure 1) Carbon dioxide (CO2) Carbon dioxide enters the atmosphere through
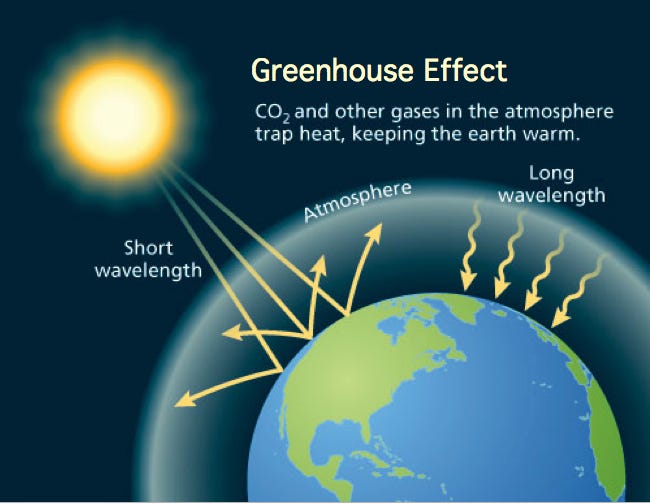



Post 5 Croatia There Is A Large Correlation Between By Monica Browne Europe At Mizzou Medium




The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids
This graph shows the heating imbalance in watts per square meter relative to the year 1750 caused by all major humanproduced greenhouse gases carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, chlorofluorocarbons 11 and 12, and a group of 15 other minor contributorsThis diagram illustrates the flow of energy through Earth's atmosphere It shows how energy contained in sunlight warms our planet, and how this energy becomes temporarily trapped as it flows away from Earth's surface as longwave infrared radiation This energy trap produces the greenhouse effect, the main driver of global warmingName greenhouse effect is often used to describe this process, in which solar energy warms the Earth, and Earth emitted IR is absorbed to warm the troposphere (This is sometimes called the atmospheric effect) The greenhouse effect is one of the most hotly debated environmental issues of our day But some background and history are in order




How To Draw A Diagram Of Green House Effect Global Warming Easy Youtube




Atmosphere Climate Environment Information Programme
Main article The natural atmosphere is composed of 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 09% argon, and only about 01% natural greenhouse gases Although a small amount, these greenhouse gases make a big difference they are the gases that allow the greenhouse effect to exist by trapping in some heat that would otherwise escape to space Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone, trap the heat that reflects back from the surface inside Earth's atmosphere The greenhouse gases that humans do emit directly in significant quantities are Carbon dioxide (CO2) Accounts for around threequarters of the warming impact of current human greenhousegas
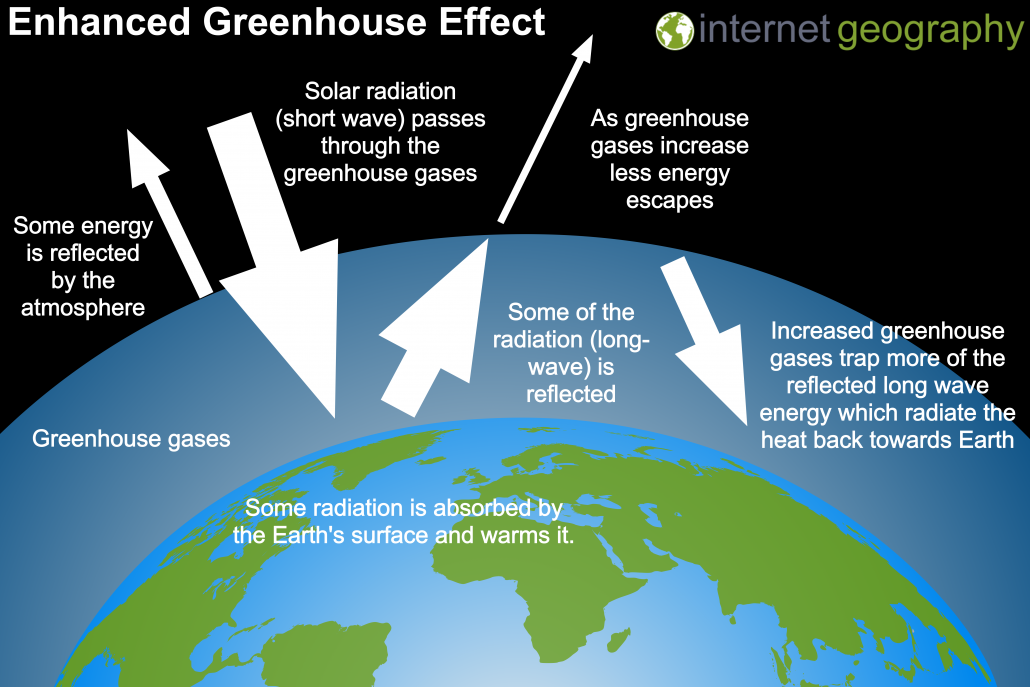



What Causes Climate Change Internet Geography




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica
The concentration of greenhouse gases can make the atmosphere essentially opaque in a particular band If the atmosphere absorbs 100 percent of the radiation in a band the absorption will not be increased when additional greenhouse gases are added In the diagram below the increase from A to B produces a much bigger impact on the proportionThe enhanced greenhouse effect What has scientists concerned now is that over the past 250 years, humans have been artificially raising the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere at an everincreasing rate, mostly by burning fossil fuels, but also from cutting down carbonabsorbing forests
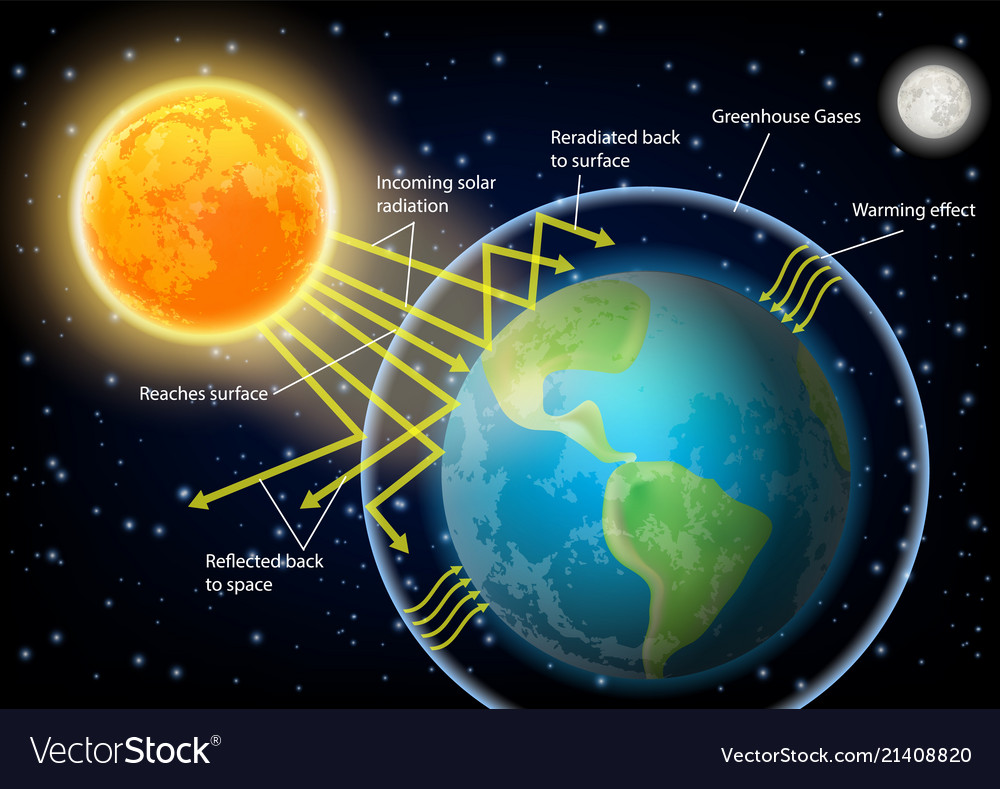



Greenhouse Effect Diagram Royalty Free Vector Image




2 Schematic Of The Greenhouse Effect From 16 Download Scientific Diagram
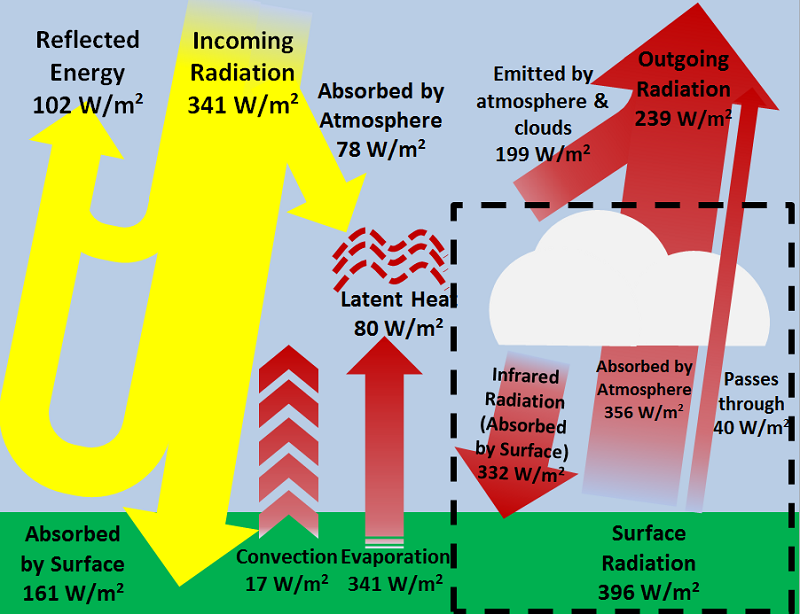



The Greenhouse Effect And Earth S Energy Budget Energy Education




The Greenhouse Effect Explained




Italki Ielts Writing Task 1 Answer 22 The Diagram Illustrates How Solar Energy Is Trapped By Greenhouse E




Greenhouse Effect Bioninja




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Creating A Greenhouse Effect Diagram




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect



Untitled Document




What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa



Q Tbn And9gcs3 Vn3xnwnq9ifctpyrsa2ofh2ymxfw2rxlcy7frr77uflqr Usqp Cau



Greenhouse Gases




Percentage Of Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Download Scientific Diagram
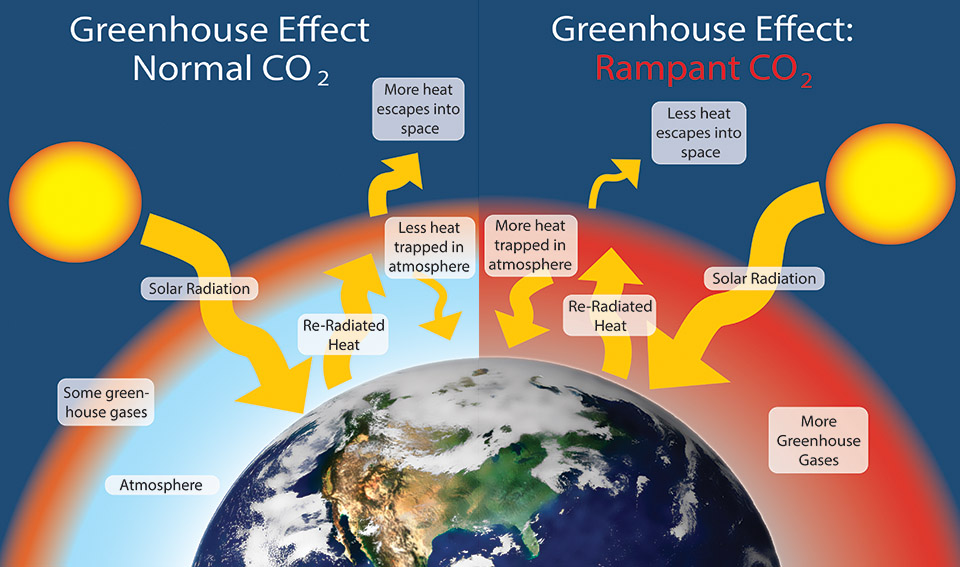



What Is Climate Change Golden Gate National Recreation Area U S National Park Service
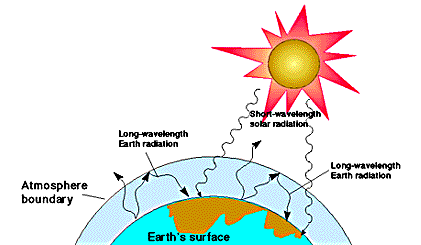



Greenhouse Effect Its Causes And Effect List Of Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




The Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Brian Williams
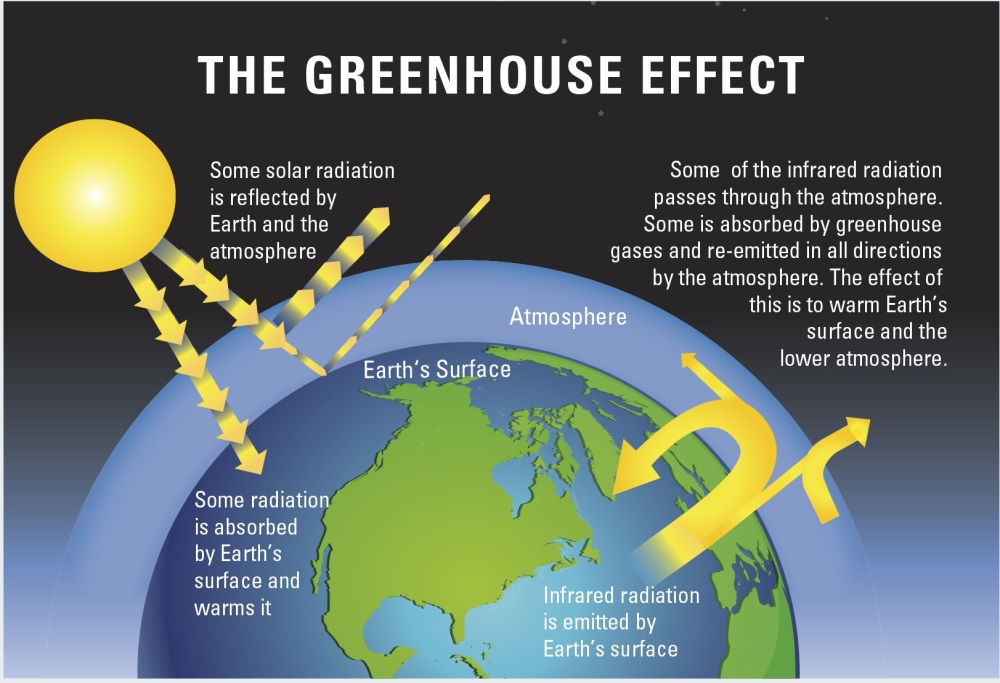



What Is The Relationship Between Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Socratic



Q Tbn And9gctoyncs8qyvzsnlf0ehywfdbiqsqkgodl5exlpxd0mjwanu7ugb Usqp Cau
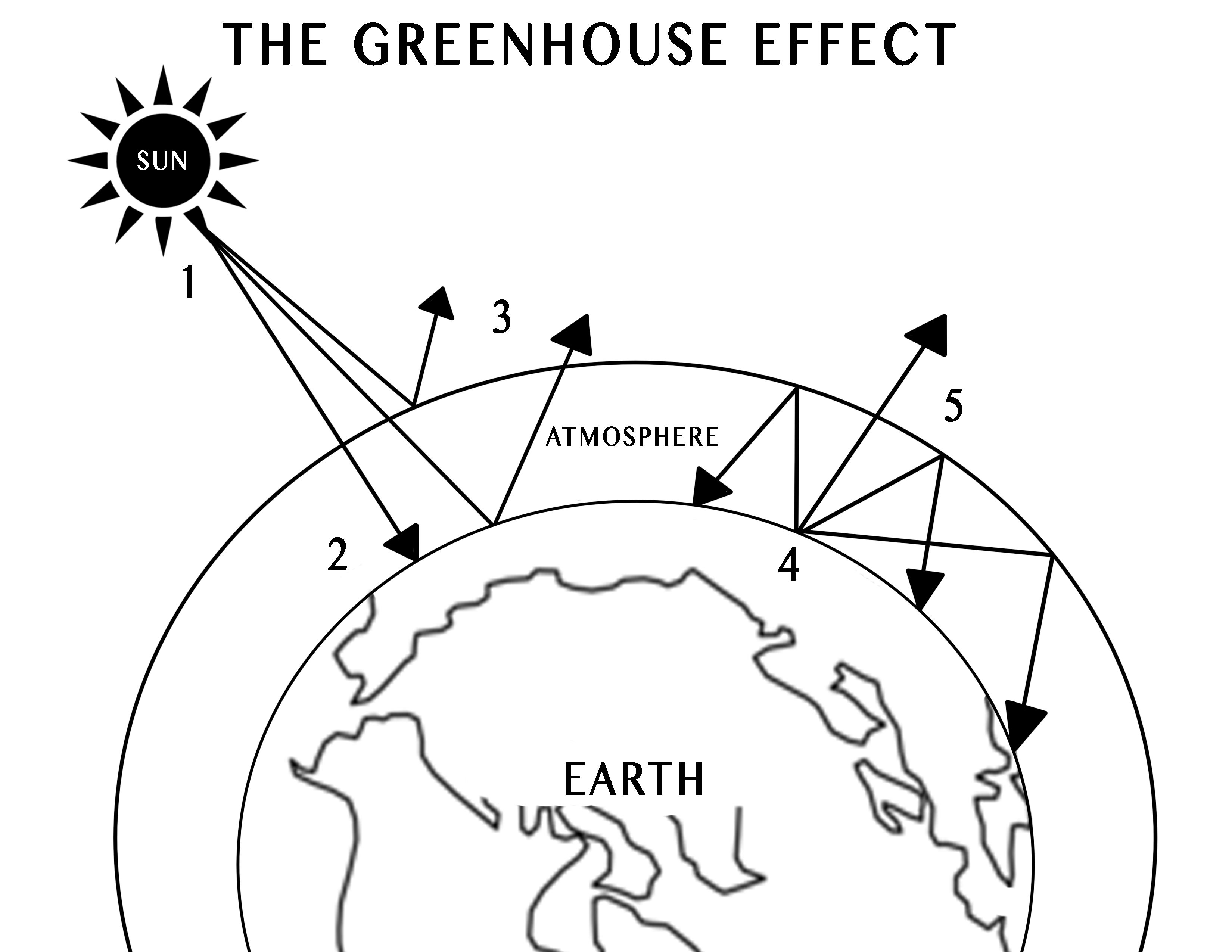



Iv Using Central Ideas About Light And Thermal Phenomena To Explain The Greenhouse Effect Exploring Physical Phenomena



Greenhouse Valearthproject



The Greenhouse Effect




The Greenhouse Effect Experiment And Lesson For Kids




Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations 149 Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




The Greenhouse Effect Diagram Quizlet
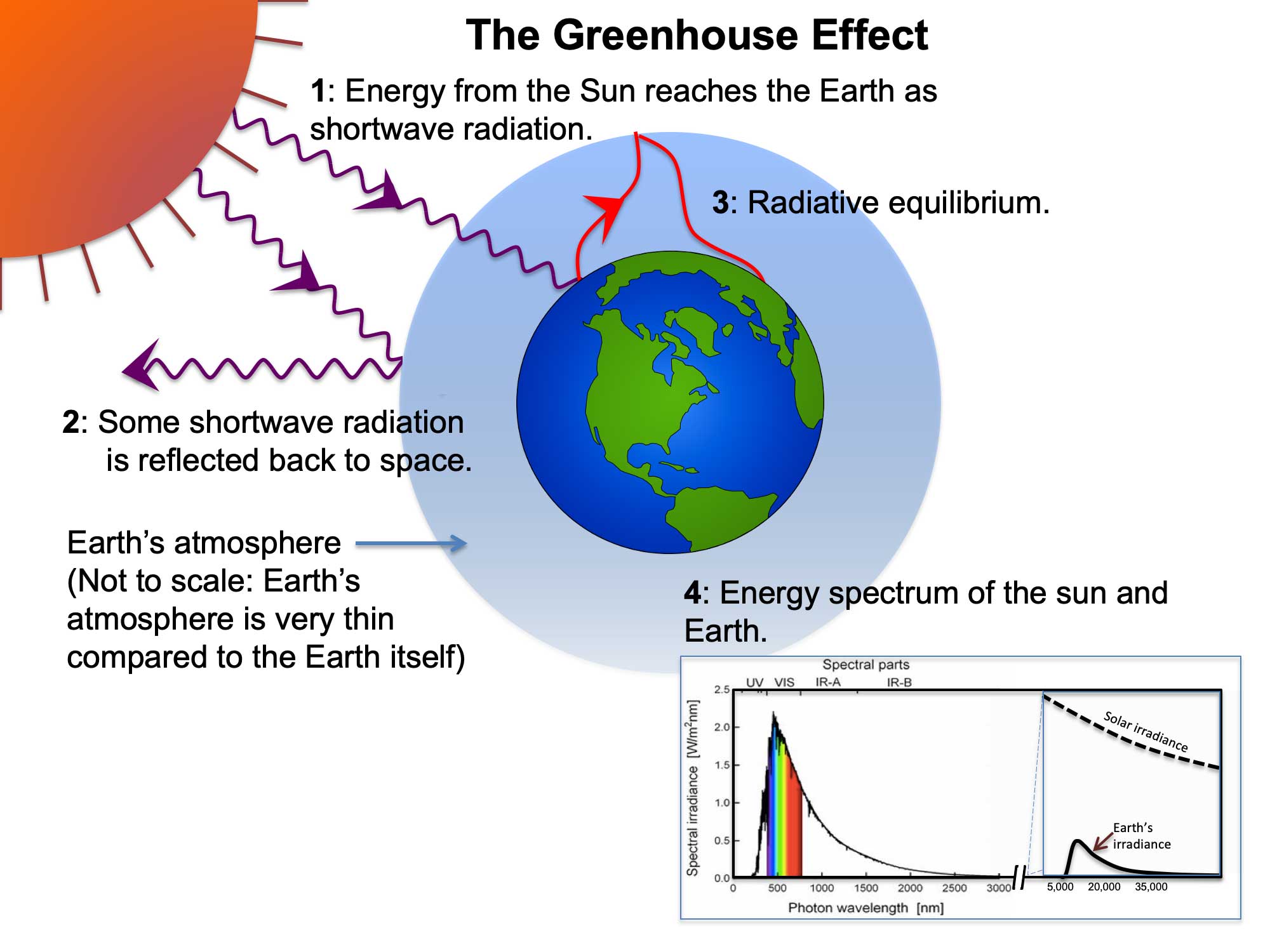



Greenhouse Gases And Global Temperature Earth Home



Shs Aice Environmental Management 4 3 2 The Atmosphere Kq3 Greenhouse Gases And Climate Change




The Greenhouse Effect Download Scientific Diagram
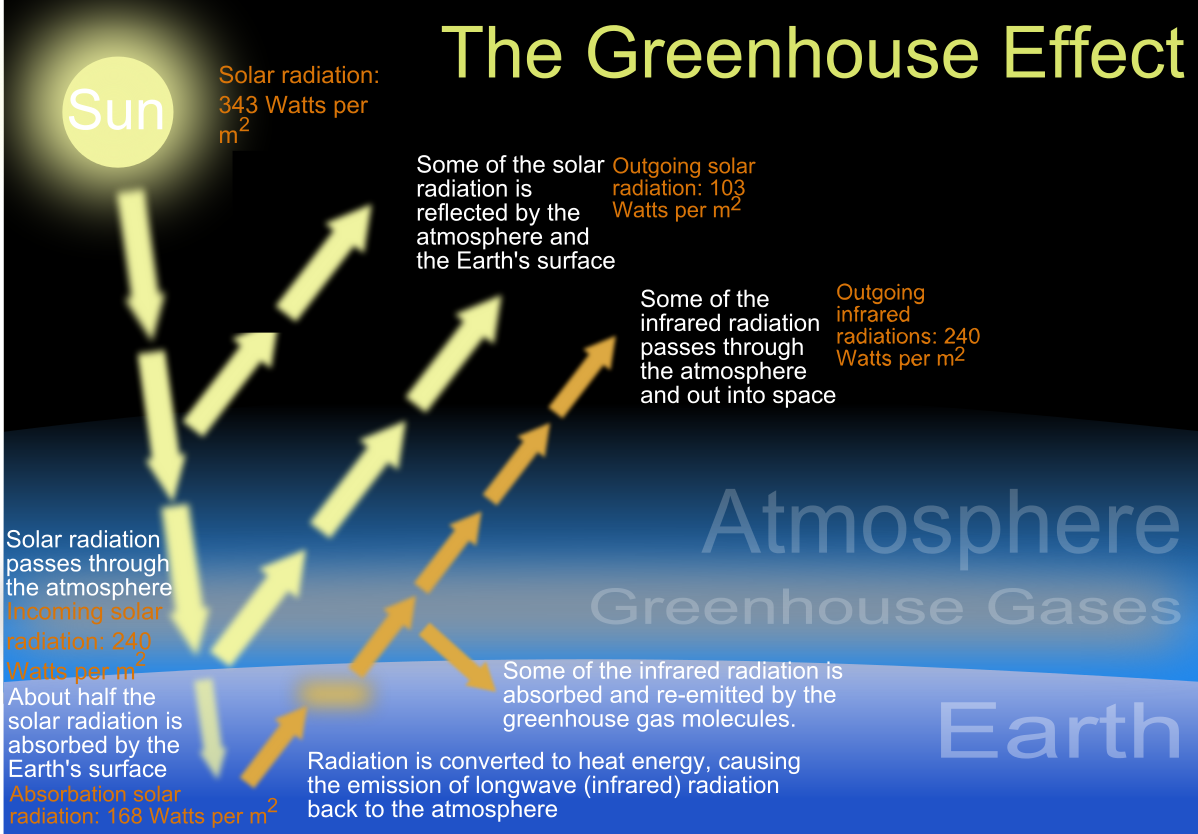



File The Green House Effect Svg Wikimedia Commons




Atmosphere Climate Environment Information Programme



Http Gzscienceclassonline Weebly Com Uploads 1 1 3 6 The Greenhouse Effect Year 9 Gz Pdf



3




Greenhouse Effect



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja



7 H The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Illustrated



Igcse Chemistry 17 2 13 Know That Carbon Dioxide Is A Greenhouse Gas And That Increasing Amounts In The Atmosphere May Contribute To Climate Change




Causes And Consequences Of A Warming Planet Agricultural Marketing Resource Center




Greenhouse Effect Teaching Box Ucar Center For Science Education




Greenhouse Effect Ck 12 Foundation




Greenhouse Gases And The Greenhouse Effect Kids Environment Kids Health National Institute Of Environmental Health Sciences



What Are The Five Greenhouse Gases Quora




Greenhouse Effect Scheme Diagram Showing How Stock Vector Royalty Free




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa
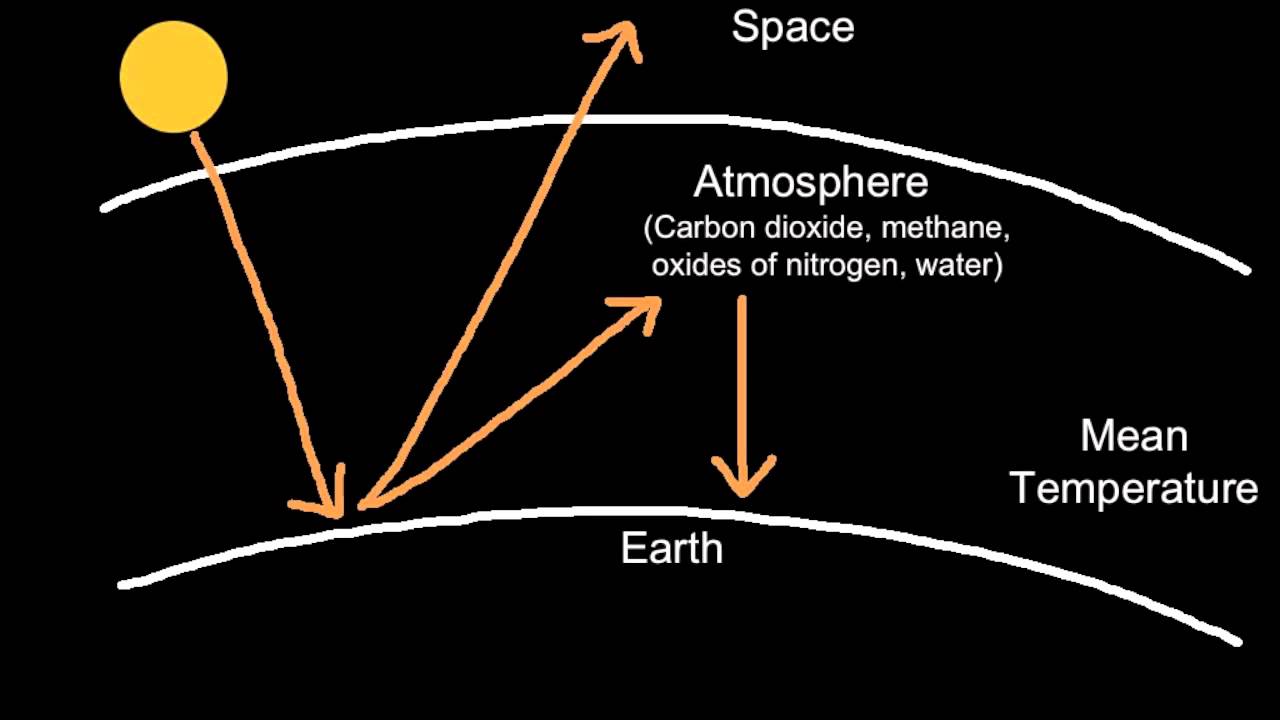



5 2 3 Explain The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Youtube
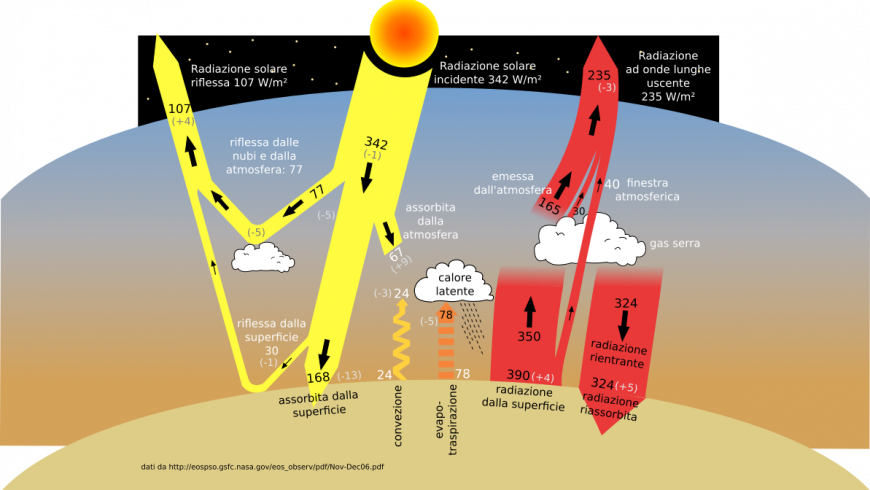



Greenhouse Gases What Are They What Can We Do To Reduce Emissions



Greenhouse Gases Effect On The Climate And Climate Change




Greenhouse Atmosphere Let S Heat Things Up Lesson Teachengineering
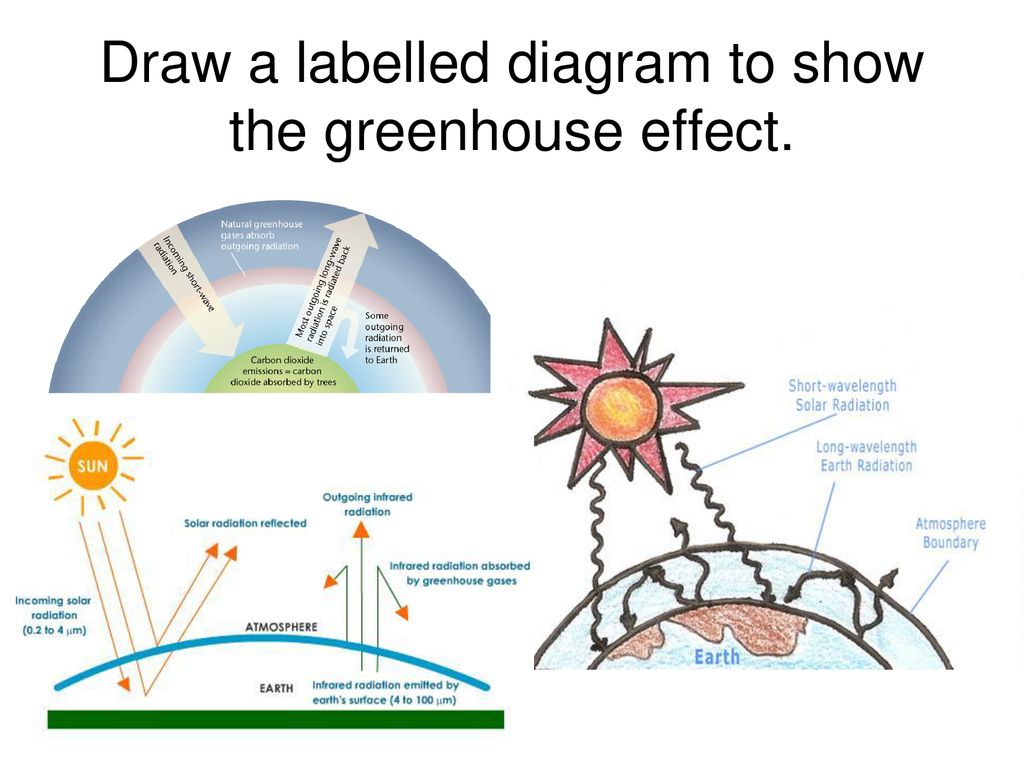



Lesson Ppt Download
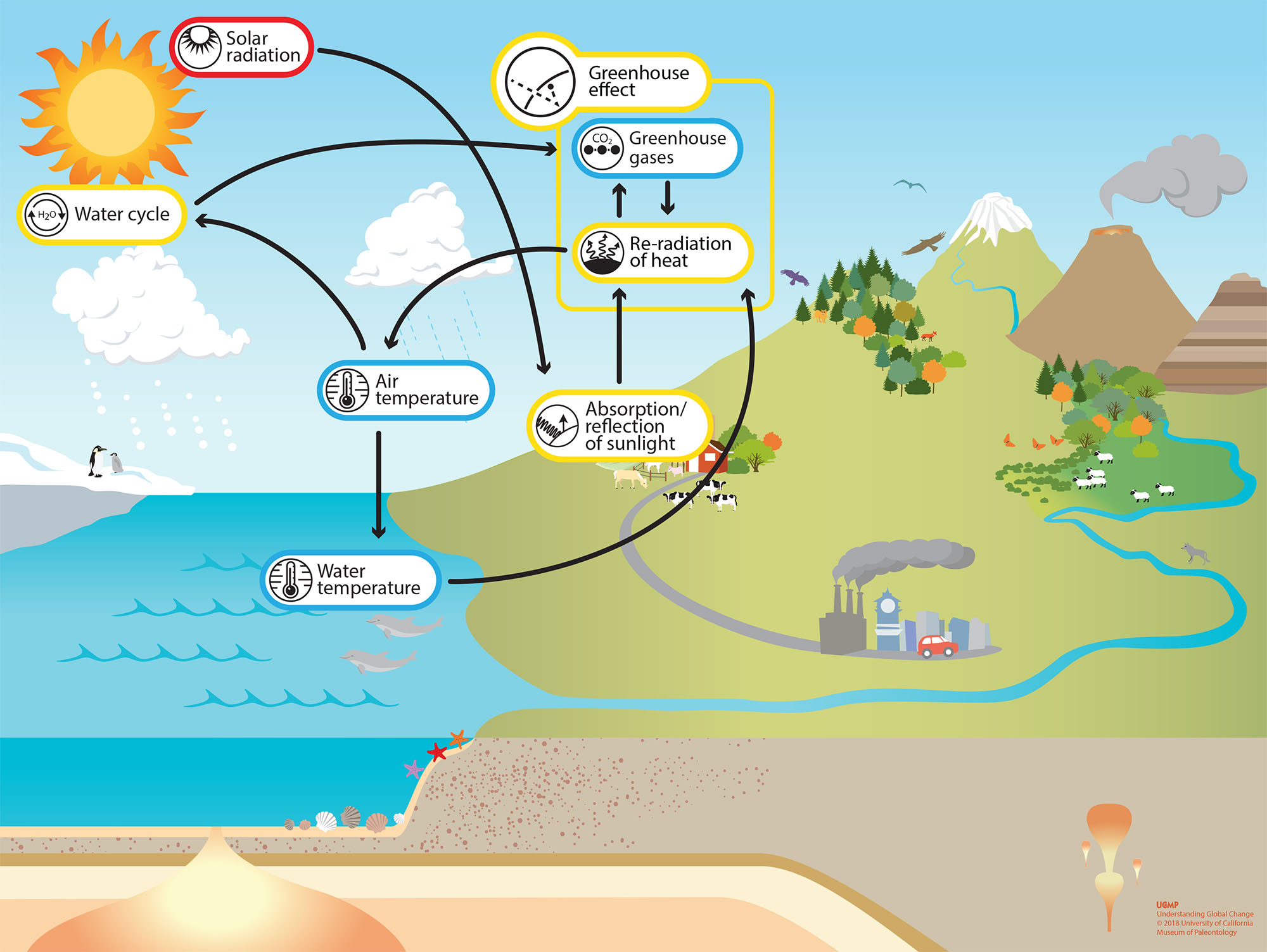



Greenhouse Effect Understanding Global Change



Greenhouse Effect Educate Inspire Space Awareness




Normal Greenhouse Effect Responsible For Maintaining Constant Download Scientific Diagram



How Greenhouse Gases Influence Climate The Weather Gamut




Greenhouse Effect Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central
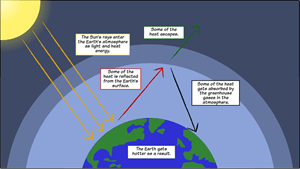



Creating A Greenhouse Effect Diagram




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




Greenhouse Effect High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




The Greenhouse Effect Climate Matters
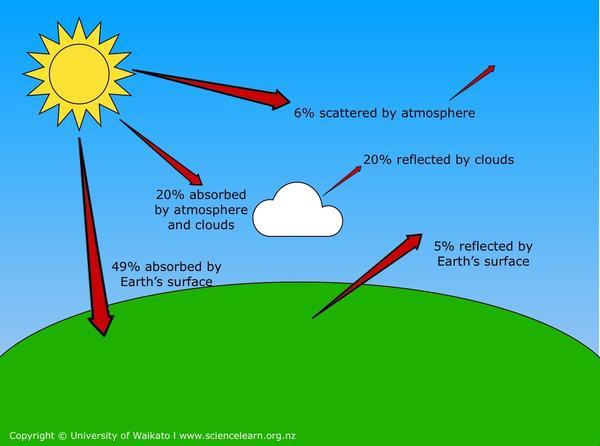



Greenhouse Effect Science Learning Hub




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc



c News



The Greenhouse Effect The Atmosphere Siyavula



Www Chicagobotanic Org Downloads Nasa Unit 1 Grades 7 9 Activity 1 3 Greenhousegasesnaturalandhumancauses Pdf




Banning The Super Greenhouse Gas Environment All Topics From Climate Change To Conservation Dw 17 10 16




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect



1



The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿